Latest Version:
Requirements:
Windows (All Versions)
Author / Product:
Cisco Systems, Inc. / Cisco Packet Tracer (32-bit)
Old Versions:
Filename:
PacketTracer62_setup.exe
MD5 Checksum:
99f7e5e6af486e79b0564b44720a6692
Packet Tracer – Troubleshooting Standard IPv4 ACLs Addressing Table Objectives Part 1: Troubleshoot ACL Issue 1 Part 2: Troubleshoot ACL Issue 2 Part 3: Troubleshoot ACL Issue 3 Scenario This network is meant to have the following three policies implemented: Hosts from the 192.168.0.0/24 network are unable to access network 10.0.0.0/8. The packet tracer is improved in each version, a practice lab created in one version may or may not work in another version. If you do not have a practice lab built in an earlier version or have just started learning from scratch, you may consider downloading the latest version of Packet Tracer. Packet tracer configuring trunks topology addressing table device interfac switch port pc1 nic 172.17.10.21 255.255.255.0 s2 10 pc2 nic 172.17.20.22 255.255.255.
- Mar 15, 2018 Objectives. Part 1: Verify VLANs. Part 2: Configure Trunks. Trunks are required to pass VLAN information between switches. A port on a switch is either an access port or a trunk port.
- Download cisco packet tracer 6.2 for windows for free. Internet & Network tools downloads - Cisco Packet Tracer by Cisco Systems and many more programs are available for instant and free download.
Become untraceable and secure online? Then you need HMA! Pro VPN!
Cisco Packet Tracer supplements physical equipment in the classroom by allowing students to create a network with an almost unlimited number of devices, encouraging practice, discovery, and troubleshooting. The simulation-based learning environment helps students develop 21st-century skills such as decision making, creative and critical thinking, and problem-solving. Packet Tracer complements the Networking Academy curricula, allowing instructors to easily teach and demonstrate complex technical concepts and networking systems design.
The Packet Tracer software is available free of charge only to Networking Academy instructors, students, alumni, and administrators that are registered Academy Connection users.
Cisco Packet Tracer supports the following protocols:
Application
FTP, SMTP, POP3, HTTP, TFTP, Telnet, SSH, DNS, DHCP, NTP, SNMP, AAA, ISR VOIP, SCCP config and calls ISR to command support, Call Manager Express.
Transport
TCP and UDP, TCP Nagle Algorithm & IP Fragmentation, RTP.
Network
BGP, IPv4, ICMP, ARP, IPv6, ICMPv6, IPSec, RIPv1/ v2/ng, Multi-Area OSPF, EIGRP, Static Routing, Route Redistribution, Multilayer Switching, L3 QoS, NAT, CBAL, Zone-based policy firewall and Intrusion Protection System on the ISR, GRE VPN, IPSec VPN.
Network Access Interface
Ethernet (802.3), 802.11, HDLC, Frame Relay, PPP, PPPoE, STP, RSTP, VTP, DTP, CDP, 802.1q, PAgP, L2 QoS, SLARP, Simple WEP, WPA, EAP.
Also Available: Download Cisco Packet Tracer for Mac
2.2.2.4 Packet Tracer – Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes
From year to year, Cisco has updated many versions with difference questions. The latest version is version 6.0 in 2018. What is your version? It depends on your instructor creating your class. We recommend you to go thought all version if you are not clear. While you take online test with netacad.com, You may get random questions from all version. Each version have 1 to 10 different questions or more. After you review all questions, You should practice with our online test system by go to 'Online Test' link below.
| Version 5.02 | Version 5.03 | Version 6.0 | Online Assessment |
| Chapter 2 Exam | Chapter 2 Exam | Chapter 2 Exam | Online Test |
| Next Chapter | |||
| Chapter 3 Exam | Chapter 3 Exam | Chapter 3 Exam | Online Test |
| 2.2.2.4 Packet Tracer – Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes | |||
| 2.2.4.4 Packet Tracer – Configuring IPv6 Static and Default Routes | |||
| 2.2.5.5 Packet Tracer – Configuring Floating Static Routes | |||
| 2.3.2.3 Packet Tracer – Troubleshooting Static Routes | |||
Packet Tracer – Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes (Answer Version)
Answer Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the Answer copy only.
Topology
2.2.2.4 Packet Tracer – Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IPv4 Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
| R1 | G0/0 | 172.31.1.1 | 255.255.255.128 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 172.31.1.194 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| R2 | G0/0 | 172.31.0.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 172.31.1.193 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 172.31.1.197 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| R3 | G0/0 | 172.31.1.129 | 255.255.255.192 | N/A |
| S0/0/1 | 172.31.1.198 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| PC1 | NIC | 172.31.1.126 | 255.255.255.128 | 172.31.1.1 |
| PC2 | NIC | 172.31.0.254 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.31.0.1 |
| PC3 | NIC | 172.31.1.190 | 255.255.255.192 | 172.31.1.129 |
Objectives
Part 1: Examine the Network and Evaluate the Need for Static Routing
Part 2: Configure Static and Default Routes
Part 3: Verify Connectivity
Background
In this activity, you will configure static and default routes. A static route is a route that is entered manually by the network administrator to create a reliable and safe route. There are four different static routes that are used in this activity: a recursive static route, a directly attached static route, a fully specified static route, and a default route.
Part 1: Examine the Network and Evaluate the Need for Static Routing
- Looking at the topology diagram, how many networks are there in total? 5
- How many networks are directly connected to R1, R2, and R3? R1 has 2, R2 has 3, and R3 has 2.
- How many static routes are required by each router to reach networks that are not directly connected? R1 needs 3 static routes, R2 needs 2 static routes, and R3 needs 3 static routes.
- Test connectivity to the R2 and R3 LANs by pinging PC2 and PC3 from PC1.
- Why were you unsuccessful? Because there are no routes to these networks on R1.
Part 2: Configure Static and Default Routes
Step 1: Configure recursive static routes on R1.
- What is recursive static route? A recursive static route relies on the next hop router in order for packets to be sent to its destination. A recursive static route requires two routing table lookups.
- Why does a recursive static route require two routing table lookups? It must first look in the routing table for the destination network and then look up the exit interface/direction of the network for the next hop router.
- Configure a recursive static route to every network not directly connected to R1, including the WAN link between R2 and R3.
- ip route 172.31.0.0 255.255.255.0 172.31.1.193
- ip route 172.31.1.196 255.255.255.252 172.31.1.193
- ip route 172.31.1.128 255.255.255.192 172.31.1.193
- Test connectivity to the R2 LAN and ping the IP addresses of PC2 and PC3.
- Why were you unsuccessful? R1 has a route to the R2 and R3 LANs, but R2 and R3 do not have a routes to R1.
Step 2: Configure directly attached static routes on R2.
- How does a directly attached static route differ from a recursive static route? A directly attached static route relies on its exit interface in order for packets to be sent to its destination, while a recursive static route uses the IP address of the next hop router.
- Configure a directly attached static route from R2 to every network not directly connected.
- ip route 172.31.1.0 255.255.255.128 Serial0/0/0
- ip route 172.31.1.128 255.255.255.192 Serial0/0/1
- Which command only displays directly connected networks? show ip route connected
- Which command only displays the static routes listed in the routing table? show ip route static
- When viewing the entire routing table, how can you distinguish between a directly attached static route and a directly connected network? The static route has an S and a directly connected network has a C.
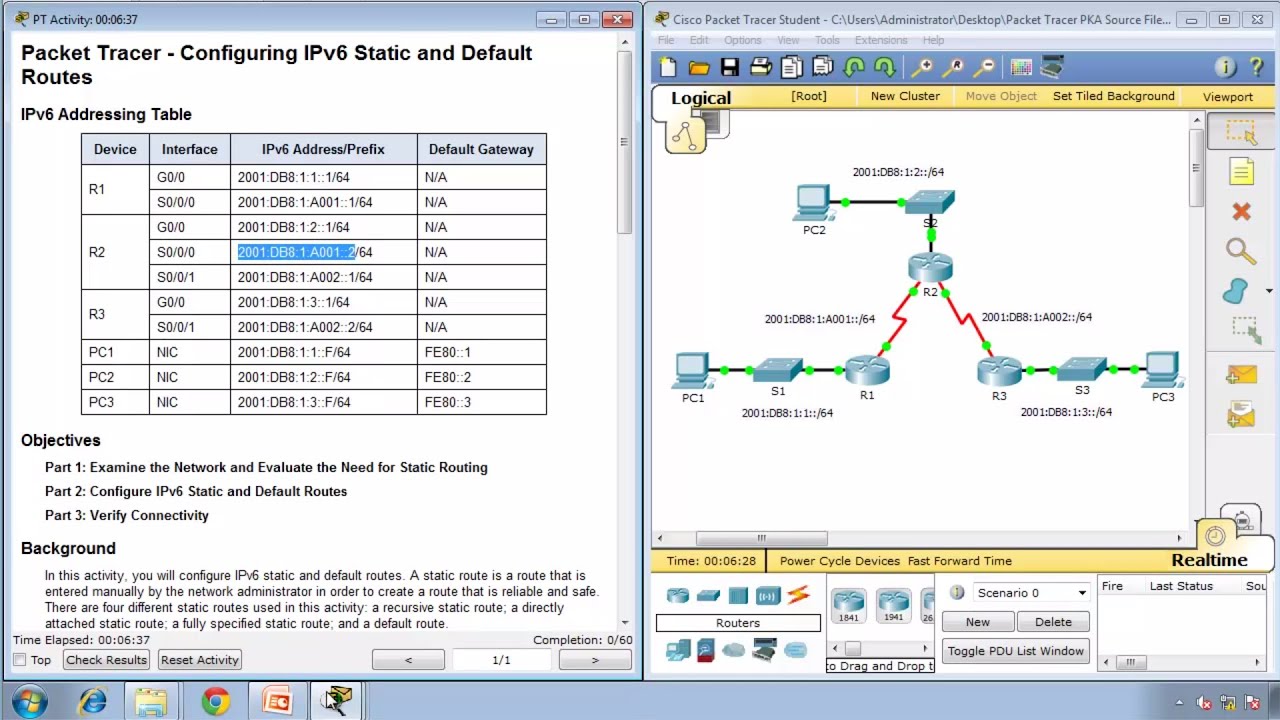
Step 3: Configure a default route on R3.
- How does a default route differ from a regular static route? A default route, also known as the gateway of last resort, is the network route used by a router when no other known route exists for a destination network. A static route is used to route traffic to a specific network.
- Configure a default route on R3 so that every network not directly connected is reachable.
- ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Serial0/0/1
- How is a static route displayed in the routing table? S* 0.0.0.0/0
Step 4: Document the commands for fully specified routes.
Note: Packet Tracer does not currently support configuring fully specified static routes. Therefore, in this step, document the configuration for fully specified routes.
- Explain a fully specified route. A fully specified route is a static route that is configured with an exit interface and the next hop address.
- Which command provides a fully specified static route from R3 to the R2 LAN?
- R3(config)# ip route 172.31.0.0 255.255.255.0 s0/0/1 172.31.1.197
- Write a fully specified route from R3 to the network between R2 and R1. Do not configure the route; just calculate it.
- R3(config)# ip route 172.31.1.192 255.255.255.252 s0/0/1 172.31.1.197
- Write a fully specified static route from R3 to the R1 LAN. Do not configure the route; just calculate it.
- R3(config)# ip route 172.31.1.0 255.255.255.128 s0/0/1 172.31.1.197
Step 5: Verify static route configurations.
Use the appropriate show commands to verify correct configurations.
Which show commands can you use to verify that the static routes are configured correctly? show ip route, show ip route static, and the show ip route [network] commands
Part 3: Verify Connectivity
Every device should now be able to ping every other device. If not, review your static and default route configurations.
From year to year, Cisco has updated many versions with difference questions. The latest version is version 6.0 in 2018. What is your version? It depends on your instructor creating your class. We recommend you to go thought all version if you are not clear. While you take online test with netacad.com, You may get random questions from all version. Each version have 1 to 10 different questions or more. After you review all questions, You should practice with our online test system by go to 'Online Test' link below.
| Version 5.02 | Version 5.03 | Version 6.0 | Online Assessment |
| Chapter 2 Exam | Chapter 2 Exam | Chapter 2 Exam | Online Test |
| Next Chapter | |||
| Chapter 3 Exam | Chapter 3 Exam | Chapter 3 Exam | Online Test |
| 2.2.2.4 Packet Tracer – Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes | |||
| 2.2.4.4 Packet Tracer – Configuring IPv6 Static and Default Routes | |||
| 2.2.5.5 Packet Tracer – Configuring Floating Static Routes | |||
| 2.3.2.3 Packet Tracer – Troubleshooting Static Routes | |||
Suggested Scoring Rubric
Packet Tracer 6.2.2.4 Configuring Eigrp
| Activity Section | Question Location | Possible Points | Earned Points |
| Part 1: Examine the Network and Evaluate the Need for Static Routing | a – d | 10 | |
| Part 1 Total | 10 | ||
| Part 2: Configure Static and Default Routes | Step 1 | 7 | |
| Step 2 | 7 | ||
| Step 3 | 3 | ||
| Step 4 | 10 | ||
| Step 5 | 3 | ||
| Part 2 Total | 30 | ||
| Packet Tracer Score | 60 | ||
| Total Score | 100 | ||
